Test Inspiration: Recently, the University System of Georgia experienced a surge in cybersecurity attacks targeting employee pay through direct deposits. Cybercriminals used phishing emails to obtain credentials and DUO codes, allowing them to alter direct deposit information and cause financial loss. Employees affected by such fraud are advised to report the theft to law enforcement, as the University cannot reissue misdirected payments.
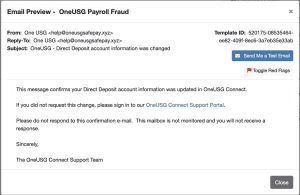
Phishing test email that GHC Information Security used.
Phishing Email Context: The phishing email designed for this test mimicked an official notification from OneUSG about a change in Direct Deposit account information. It used personalization elements such as the OneUSG logo and posed as “One USG Support Team.” If you hovered over the link, you would see that it directed you to the malicious domain “oneusgsafepay[.]xyz.” The design and content were tailored to look authentic, making it challenging for users to distinguish it from a legitimate OneUSG notification.
Payroll fraud is a type of scam where cybercriminals attempt to steal employees’ payroll information, such as direct deposit details, by sending fraudulent emails that appear to be from legitimate sources. These emails often contain links to fake websites designed to capture login credentials or other sensitive information. The goal is to redirect employees’ paychecks to accounts controlled by the fraudsters. Recognizing and reporting these phishing attempts is crucial to protecting personal and organizational financial information.
Key Findings & Recommendations:
- Email Address Discrepancies: Be cautious with emails that appear genuine but have slightly altered addresses. Cybercriminals often use domains that resemble the authentic one with minor changes.
- Suspicious Links & Attachments: Always approach links or attachments in unsolicited or unexpected emails with suspicion. They are common phishing tactics.
- Verify Links: Before engaging with any link, hover over it to inspect the actual URL. Ensure it directs to a legitimate site and be alert for any anomalies like misspellings or odd domain extensions.
- Check for Personalization: Authentic communications, especially from platforms like OneUSG, will often be personalized. Beware of generic greetings.
- Stay Updated: With cybercriminals constantly refining their methods, it’s crucial to stay updated on the latest phishing strategies and partake in regular awareness training.
- Report Suspicious Emails: If you encounter a dubious email, refrain from interacting and promptly report via the Phish Alert button.
Conclusion: The landscape of phishing is continuously changing. By staying informed about cybercriminals’ tactics and maintaining a vigilant approach, we can substantially mitigate the risk of succumbing to these threats.